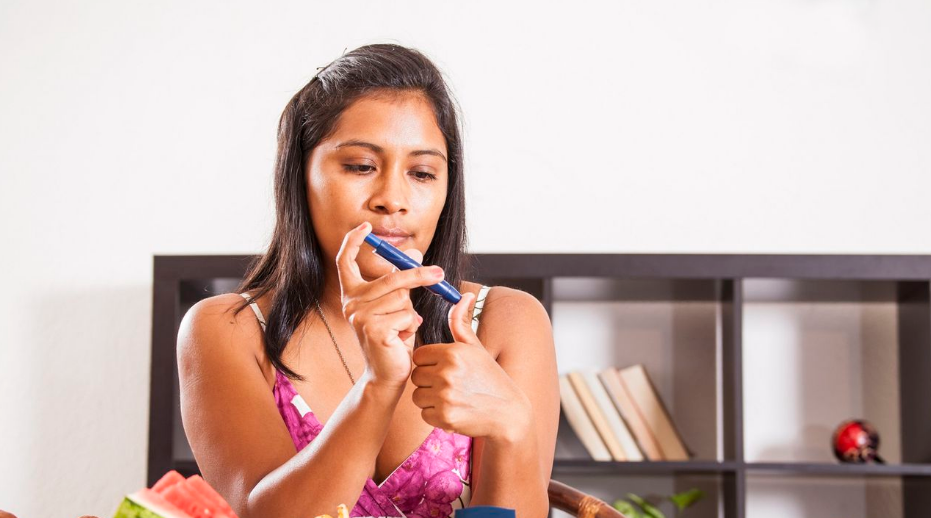
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs when the pancreas does not secrete enough insulin or when the body does not effectively use the insulin it produces.
The importance of this hormone lies in the fact that it is responsible for regulating the concentration of glucose in the blood, that is, the level of sugar in the blood. The World Health Organization notes on its web page that “a common effect of uncontrolled diabetes is hyperglycemia (i.e. high blood glucose), which over time causes severe damage to many organs and systems in the body, especially nerves and blood vessels”.
The medical encyclopedia MedlinePlus explains that people with diabetes have high blood sugar because their bodies are unable to move sugar from the blood into muscle and fat cells to burn or store as energy.
Another scenario is when the liver makes too much glucose and excretes it into the blood. In this case, there are two reasons: the pancreas does not produce enough insulin, the cells do not respond normally to insulin, or both conditions are met.
To understand how this condition behaves and what the most effective treatment is, you first need to determine what type of diabetes you have. Therefore, it is necessary to consult a health professional, so that the patient is guided towards an accurate diagnosis.
- Type 1 diabetes: characterized by a lack of insulin production and requires daily intake of this hormone.
- Type 2 diabetes: is caused by the ineffective use of insulin by the body. More than 95% of diabetics suffer from type 2 diabetes, which is largely due to being overweight and lacking in physical activity.
- Gestational diabetes: arises during pregnancy and corresponds to hyperglycemia values that, although higher than normal, are lower than those determined for the diagnosis of diabetes.
Diabetes is a chronic disease, that is, of long duration. Its symptoms vary according to the type and characteristics of each individual. Furthermore, it is accompanied by multiple health risks. Therefore, their care is essential to avoid future complications such as: eye problems, ulcers and infections in the lower extremities, damage to the body’s nerves, kidney problems, weakened immune system and increased risk of heart attack or stroke.
Basic Diabetes Care
With the arrival of 2023, many people are eager to take care of their health, thus fulfilling one of the most popular New Year’s resolutions. According to a MedlinePlus review, “Treatment for type 1 and type 2 diabetes consists of nutrition, activity, and medication to control blood sugar.”
Likewise, “getting better control of blood sugar, cholesterol and blood pressure levels helps reduce the risk of kidney disease, eye disease, nervous system disease, heart attack and stroke,” adds the said portal.
For its part, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) shares some tips for people with diabetes to take care of their condition:
Monitor your Blood Sugar Level
Take an A1C test regularly to monitor your average blood sugar level (every three months).
Stop Smoking
According to the NIDDK, abstaining from smoking is especially important for people with diabetes, because both smoking and diabetes reduce the diameter of blood vessels. Narrowing of blood vessels makes the heart work harder.
Here are some of the benefits of giving up cigarettes (including e-cigarettes):
- Reducing the risk of heart attack, stroke, neurological disease, kidney disease, diabetic eye disease and amputation.
- Improve cholesterol levels and blood pressure.
- improve blood circulation.
- It’s easier to stay physically active.
Take Care of The Food
Implement a good diabetes diet, for example: fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, skinless chicken or turkey, fish, lean meat, skim or low-fat milk, and cheese. Also, it is better to drink water instead of sodas or products that contain added sugar.
As diabetics must take care of cholesterol levels, it is appropriate that the diet prioritize low-calorie foods, saturated fats, trans fats, sugar and salt.